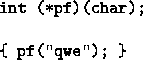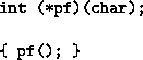- Bad function definition for an illegal form which
looks like a function definition.
f{}
- function initialized as a variable.
f(){} = 1;
- missing declared argument <varname> when an
input parameter is not in the parameter list.
f(a) int a,b;{} /* missing declared argument b */
- redeclaration of <varname>
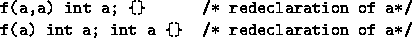
- the function returns no value when a function as
declared void attempts to return a value.
void novalue() { return 1; }
- the function returns a value when a function
declared returning a value attempts to return no value.
int value() { return; }
- incompatible return type when the returned value
type and declared returned type are inconsistent.
int badvaluetype() { return badvaluetype; }
- illegal function call
{ 1(); }
- ? arguments for <functionname>, ? required
and ? arguments for <functionname>, at least ?
required when you call a function with a wrong number of
arguments.
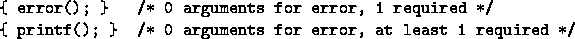
- incompatible type for <functionname>
argument ?,<type1> <> <type2>
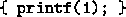
(incompatible type for print argument 1, char * <> int )
- incompatible type argument ?, <type1> <>
<type2>, as previously but in this case the function is
executed.
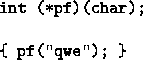
- ? arguments at least ? required when the number of
argument of a computed function is insufficient. In this case
does not test the equality of the number of arguments
and the declared number at reading time, because the function
has perhaps a variable number of arguments (as printf).
Therefore check is performed at run time.
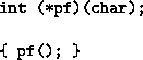
![]()
![]()
![]()